Nepal Rastra Bank (NRB) has launched Nepal Financial Inclusion Portal. The portal provides real-time information and data to figure out a realistic picture of financial access and its usage in Nepal.
The portal (emap.nrb.org.np) was launched by NRB with the support of the United Nations Capital Development Fund (UNCDF).
Technology and financial literacy are the right vehicles to promote and enhance financial inclusion. By measuring financial inclusion and generating analytical reports, Nepal Financial Inclusion Portal aims at providing real-time information and data to map out a realistic picture of the financial access and usage. This will ultimately facilitate data-driven policy intervention.
Key features of Nepal Financial Inclusion Portal
1. Key financial inclusion indicators
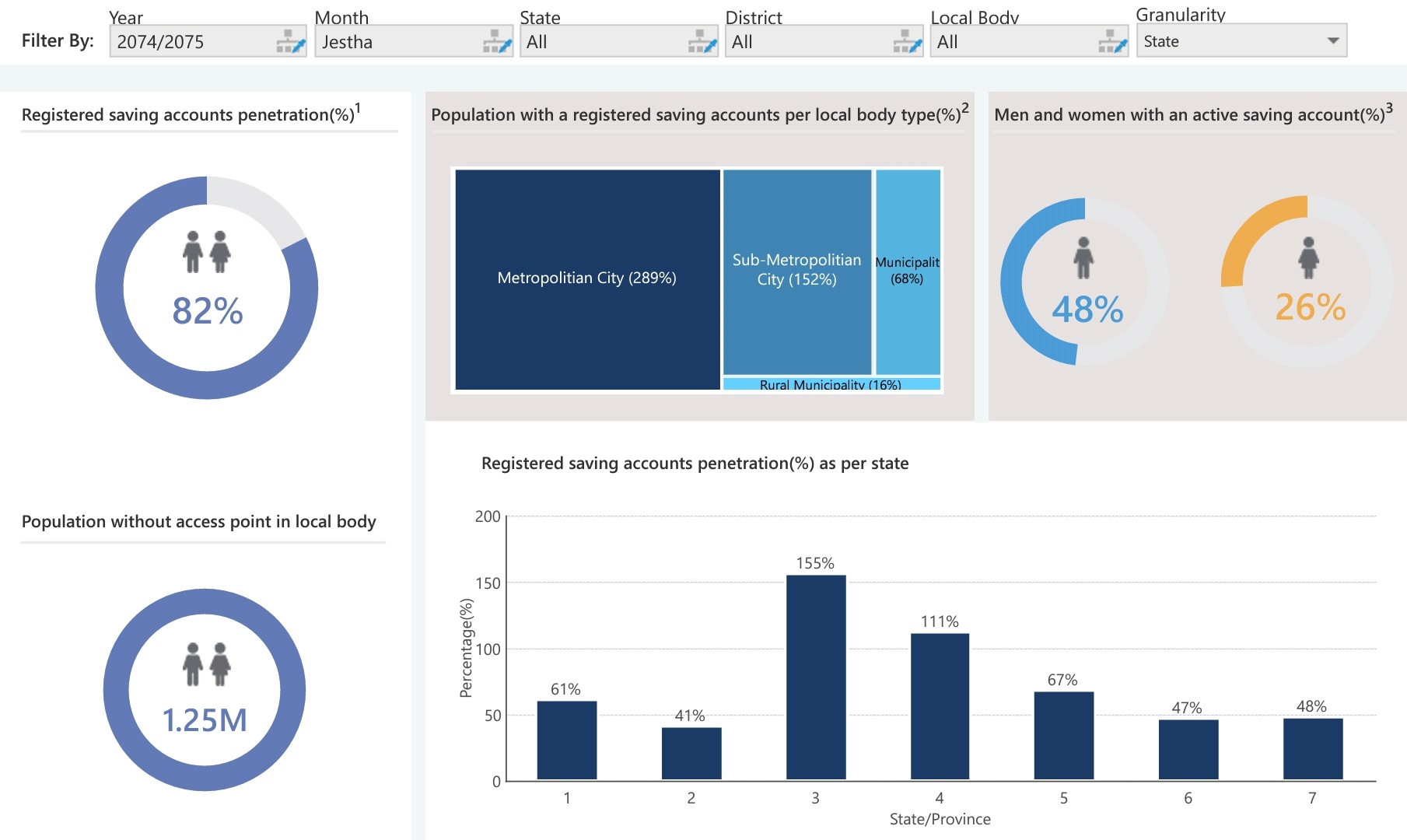
Registered savings account penetration, population with savings accounts per local body, men and women with an active saving account
2. Access to financial service
Number of access points in a state/district/local body, average population served per access point, access to a density map, the share of access points per class of institution, number of access points per class of institution
3. Usage of financial services
Savings accounts usage, savings account activity rate, savings account activity rate per local body, active and registered payment instruments per type of services
4. Credit and deposit
Total credit amounts, the average amount per saving account, total outstanding credit per class of institution, the total amount in saving accounts per class of institution
5. Branchless banking (BLB) agents
BLB agents’ penetration, average number of accounts per agent, BLB agent activity rate
Furthermore, the portal allows users to export the data in Excel and PDF format for further study.
Benefits of Nepal Financial Inclusion Portal
1. The portal enables commercial banks, development banks, finance companies, microfinance companies, and non-bank payment service providers to report their data in a systematic manner.
2. It will provide information and data from remote parts of the country where the government and regulators can’t react immediately. Availability of data on financial access will help the government and the central bank for policy intervention, targeting rural areas.
3. The portal will help both the government and central bank to develop financial infrastructure to increase people’s access to financial services which is a must for the economic growth of the country.
4. It would also support all central, provincial, and local governments to make economic development sustainable and ensure that locals are able to have complete access to government services.
Read also: Financial Inclusion: Where does Nepal stand?