In the initial stage of the banking system in Nepal, usage of ICT was limited mainly to back-office operations. With the advancement of technology, the adoption of the internet and mobile phone has become common. Customers can now use mobile devices and the internet to do their banking operations without visiting bank branches.
Following digital and ICT-enabled banking delivery channels are provided by banks in Nepal:
1. Internet Banking
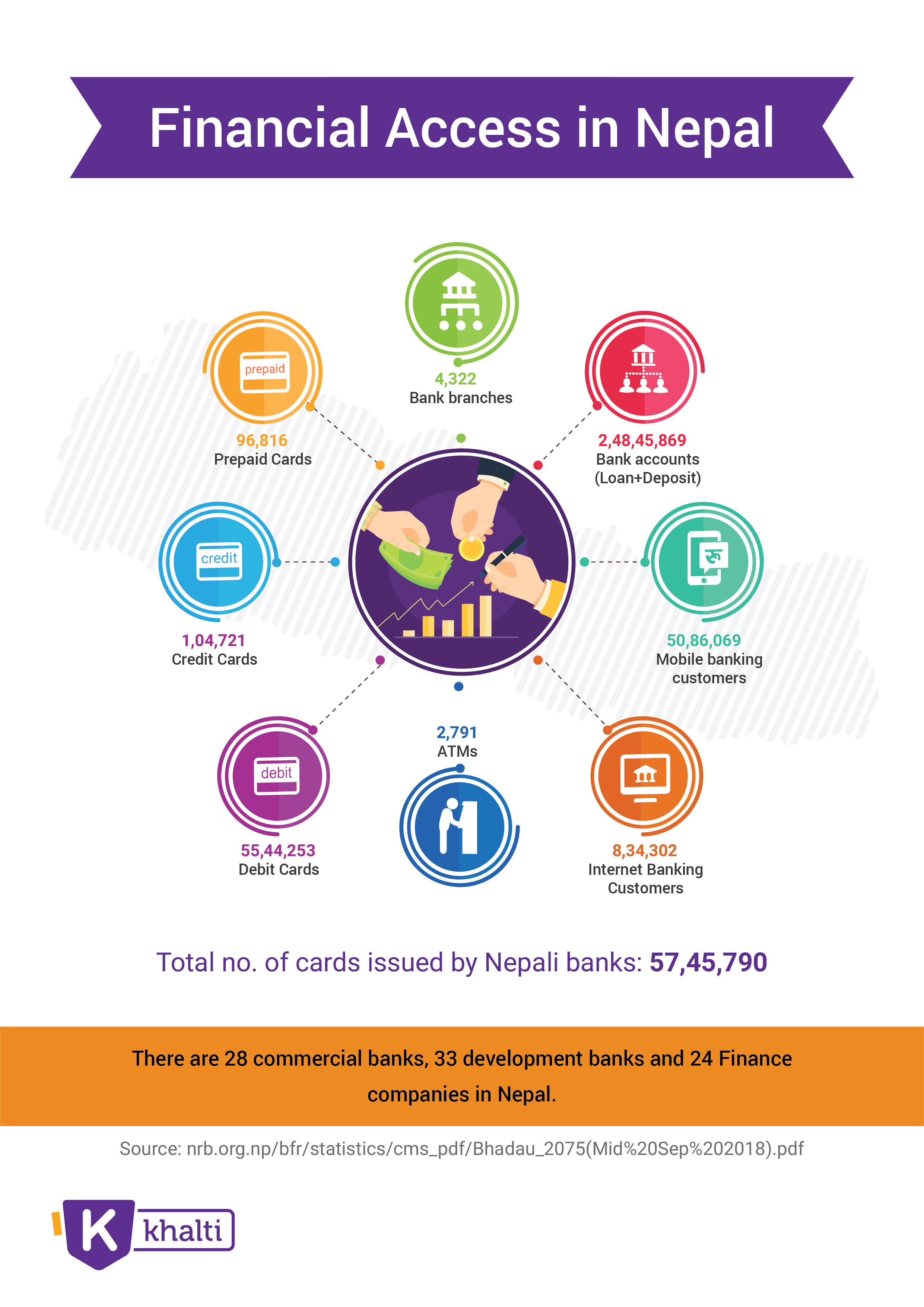
This service allows customers subscribing to internet banking service to do banking by using the internet from their PC, laptops, and mobile, among others. Depending on the service offered by the bank, customers may be able to view their account information, transfer funds from one account to another, and pay bills. Subscribers may also communicate with the bank to request some banking operations. Internet banking service was first started in Nepal by Kumari Bank Limited in 2002 which at present, is offered by most of the commercial banks. There are 8,34,302 internet banking subscribers in the Nepalese financial industry as of mid-September 2018.
2. Mobile Banking
This service allows customers to perform their banking operations by using a mobile hand-held device. Message transfer is typically sent via SMS from a mobile hand-held device to the bank’s system. Typical services offered by this service are fund transfer, account information view, communication with the bank, bill payment, and mobile Top Up, among others. Laxmi Bank Limited first started this service in Nepal in 2004 and now most of the class “A” banks offer this service. As of mid-September 2018, there are 50,86,069 mobile banking customers in Nepal.
Read details: Over 5 Million Use Mobile Banking In Nepal
3. Plastic Cards
This is another widely used electronic banking channel. Plastic cards are available in the form of prepaid, debit, and credit cards. Such cards can be used to withdraw money, pay bills by ATM and POS machine, and make payments for purchased goods online, among others. The plastic card holds data in the magnetic stripe at the back of the card but this technology is being replaced by a chip-based, more secured EMV card. The plastic card as a credit card was first introduced in Nepal by Nepal Arab Bank Limited (now NABIL bank) in 1990. There are 55,44,253 subscribers of debit cards, 1,04,721 subscribers of credit cards, and 96,816 subscribers of prepaid cards in Nepal as of mid-September 2018.
Nepalese banks also issue plastic cards that can be used in international ATM and POS machines. Currently, VISA, SCT, and Master Card plastic cards are issued by Nepalese banks, which also acquire cards issued by international banks. Nepalese banks, which issued magnetic stripe-based cards initially, have now started issuing EMV cards.
4. Automated Teller Machine and Point of Sale Machine
ATM is a device used to withdraw cash; it can also be used to make payments of bills. In Nepal, Himalayan Bank Limited first introduced it in 1995. The number of ATMs installed is growing day by day, with the number of ATMs reaching 2,791 as in mid-September 2018. After the establishment of SCT 2001, an integrated shared network of ATMs was established. This network is allowing inter-operability of ATM Cards in ATMs and POS of different financial institutions by accepting multiple device types and acquiring standards1. Besides, there is a network of VISA that allows usage of the card of one bank in ATM of another bank.
5. Branchless Banking
This is a relatively new electronic banking product that helps to include the people who are staying in remote areas and do not have access to bank branches. Customers can access their bank account, transfer fund to other accounts, withdraw money from their account and make payments for purchasing goods and services at the Point of Transaction (POT) machine maintained by a bank or its branchless banking agent.
The service can be accessed by using plastic branchless banking cards and biometrics. Mostly, a fingerprint is taken for biometric authentication. There are 1285 branchless banking centers and 1,30,660 branchless banking customers as of mid-September 2018.
6. Mobile Wallets
This product is the latest and emerging e-banking product in Nepal. This allows customers without having a bank account to hold money in their mobile number. This can be used for the payment of goods and services. Subscribers of this product can load money from their bank accounts. This product has helped to provide banking services to customers who do not have a bank account. As the penetration of mobile devices in Nepal is high and establishing banks and bank branches is difficult due to geographical terrain, this can be a great tool for financial inclusion.